In landlord-tenant interactions, disputes about rent payment and eviction protocols and late rent eviction legalities often emerge. A common scenario involves landlords attempting to remove tenants for minor rent payment delays.
This article delves into the legal ramifications of incidents in the United States. It examines lease agreements and state-specific eviction laws. Additionally, it discusses tenants’ rights in defending against unjust eviction attempts. These attempts are often based on minor rent payment delays.
Understanding Lease Agreements And Late Rent Eviction Legalities
Overview of Lease Terms: Lease agreements define rules for landlords and tenants, including rent payment deadlines. They set the legal framework for landlord-tenant relationships and specify obligations, rights, and responsibilities for both parties.
Late Payment Clauses: Leases often include provisions detailing grace periods for rent payments, allowing tenants additional time without penalties. Late fees may also apply for payments made after the specified due date.
Legal Framework for Evictions
State Laws: Eviction procedures, subject to state laws, vary throughout the United States of America. Understanding state-specific regulations is very important. State laws, however, dictate eviction protocols, emphasizing the critical need to familiarize oneself with applicable statutes for effective engagement in legal procedures.
Notice Requirements: Landlords are legally obligated to provide tenants with adequate notice before commencing eviction processes, with the timeframe subjected to state statutes and lease agreements, ensuring compliance with legal protocols and protecting tenant rights and interests.
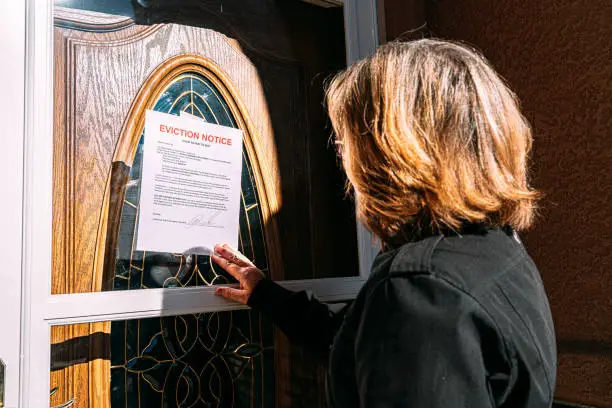

Just Cause Evictions: In certain jurisdictions, landlords must justify evictions with “just cause,” like rent non-payment or lease breaches. These requirements vary by state, ensuring fairness in tenant-landlord relations with examples such as lease violations or non-payment of rent and safeguarding tenants’ rights while maintaining landlords’ ability to enforce lease agreements.
One Day Late: Legal Implications And Late Rent Eviction Legalities
Enforcement of Lease Terms: Landlords possess the legal authority to uphold lease agreements, including stipulated deadlines for rent payments. The repercussions for delayed payment, even by a single day, vary based on the specifics outlined in the lease contract and relevant state legislation. Furthermore, these provisions outline how penalties or actions may be enforced against tenants for late rent payments.
Grace Periods: A single-day delay may not qualify as a contractual breach if a lease incorporates a grace period for rent payment. Tenants must carefully examine lease agreements to grasp stipulations concerning delayed payments. Hence, understanding these terms is crucial for tenants to avoid unintended breaches and potential legal repercussions.
Late Fees: Landlords possess the authority to levy late fees on tenants for rent payments beyond the due date, as outlined in the lease agreement. Regardless, the legality and validity of such charges are subject to compliance with relevant state legislation.
Compliance with state laws is essential to ensure the validity and implementation of late fees in landlord-tenant agreements.
Legal Option for Tenants
Communication with Landlord: Tenants encountering eviction threats due to minor rent delays should swiftly engage in dialogue with their landlord. Prompt communication can facilitate a peaceful resolution, possibly avoiding escalated legal proceedings.
Active participation promotes understanding and cooperation between parties, potentially minimizing the need for legal intervention.
Consultation with Legal Professionals: Tenants encountering uncertainty about their rights or confronting unfair eviction proceedings should promptly consult legal experts specializing in landlord-tenant law. This is because legal professionals possess the expertise to navigate complex legal frameworks, provide informed advice, and advocate for tenants’ rights.
Seeking timely guidance can empower tenants to uphold their legal protections and effectively address any unjust actions by landlords.
Defense in Court: Tenants possess the legal right to contest eviction processes through judicial means, primarily when they perceive the landlord’s conduct as illegal or inequitable.
This involves initiating legal proceedings, during which tenants can present evidence and arguments to demonstrate the eviction’s purported unlawfulness or injustice, seek redress, and potentially halt or reverse the eviction decision.
Conclusion
Landlords possess the authority to enforce lease stipulations on rent payment; however, evicting a tenant solely for one-day late rent may lack legal grounds. Tenants must familiarize themselves with lease terms and relevant state regulations concerning landlord-tenant interactions to safeguard their entitlements.
Effective communication, legal consultation, and comprehension of available legal remedies are vital for managing eviction conflicts within the United States. Thus, understanding lease agreements and local statutes empowers tenants to affirm their rights and negotiate disputes with landlords, ensuring fair treatment and compliance with legal procedures throughout eviction.