Natural disasters like hurricanes, tropical storms, or floods can drastically damage your property. Understanding laws about property damage can be a wise option. In a recent video, a roadside disaster that happened in the UAE raises many concerns. Now the interesting part comes, is it due to the flood or there is something else to the story? Read on to find out what the law dictates about it.
Basics about Property Damage
Property damage is simply the harm caused to personal or real property. It can be due to natural processes or due to individual actions. Some of its examples include residential property damage, such as homes, trees, and driveways, etc. Commercial property damage is another property damage type. Other types include personal property damage, such as vehicles and bicycles. Natural causes of property damage are wind, fire, flooding, etc.
Types of Property and Their Damage Claims
The law offices of Jay S. Knispel state that mainly there are two main categories of property according to the law: Real Property and Personal Property. Real property means the land and the structures permanently attached to it, such as buildings, homes, and vegetation. However, personal property, known as chattels, encompasses all other items like vehicles, electronics, or pictures.
Both of these properties can be harmed. Similarly, a person can file a lawsuit to compensate for the harm in New York. Normally, the amount of compensation for property damage is decided in two ways. One is selecting the lower value between the property’s market value fluctuation just before and immediately after the incident. The other is the expense of repairing or replacing it.
Types of Damage Claims
Property damage claims are legitimate concerns for property owners. You can file a lawsuit for property damage on various legal grounds.
- Carelessness
If someone behaves negligently and recklessly, disregards your real or personal property, and tries to harm it.
- Trespass to Chattels
Negligence is a state where someone accidentally damages your property. However, Trespass to Chattels is a kind of intentional tort (omission that causes injury). According to this argument, you might be able to sue someone who intentionally harms your property.
- Trespassing on Land
A property damage claim may also be based on this deliberate tort. Someone purposefully entering your property is considered a trespass to land.
- Conversion
Conversion is similar to chattel trespassing. It happens when the plaintiff’s property is in the defendant’s control. If an individual permanently takes possession of someone else’s property, it may result in conversion.
- Liability for Products
If product manufacturers sell a flawed product that damages property, they might be held accountable for that. It falls under product liability.
- Contractual Remedies
If you have property damage, you can take legal action under contract law. Insurance contracts are the most suitable example.
Property Owner’s Liability and its Negligence in Damage

Just like how one can be responsible for someone’s injury and it depends on negligence, he can also be liable for someone’s property damage. According to the Los Angeles Times, property owners were only liable for damage done by man-made circumstances in history. These circumstances can be like an unsecured board from your lumber pile being blown through your neighbor’s plate-glass window. But other forms of damage, such as falling tree limbs or other natural events on their land, did not fall under property damage. However, courts are increasingly likely to apply negligence and an ordinary standard of care in both situations.
Intentional Torts and Its Various Manifestations
According to Findlaw, a person who intentionally causes injury to another person or piece of property is guilty of a civil wrong, which is known as an intentional tort. Typical examples of deliberate behavior under tort law include:
- Battery and Assault
- Wrong imprisonment
- Defamation
- Trespassing on land (or trespassing on property)
Intentional tort claims differ from other forms of torts, such as those based on incompetence, carelessness, and product/strict liability. These additional torts involve more unintentional harm. Particularly, they include negligence torts such as wrongful death or malpractice. They typically involve acts that are not intentional but rather a lack of reasonable care that results in injury.
Click here to read a comprehensive guide about manufacturer’s liability.
Affirmative Defenses as a Legal Tool for Defendants

If you’ve been accused of misconduct, perhaps you shouldn’t refute it. However, there may be a valid cause for your behavior, which you might offer as an excuse. This is called an affirmative defense. Normally, a defendant has the burden of proof for affirmative defenses. Whereas, the plaintiff is usually responsible for proving physical harm or auto accident claims. For instance, you have to prove that you were acting in defense of others so that you will be relieved of all or some legal liability for your actions. Consent, public need, self-defense, and property protection are other prevalent affirmative defenses. In addition to tort proceedings, affirmative defenses can be utilized in criminal accusations and criminal law.
Boundaries of Property Defense
If you’re defending your house or personal belongings, some questions can come into your mind like what kinds of activities are appropriate? Compared to defending oneself or others, the use of force in property protection is more restricted. Although each has its own rules of force, state legislation sometimes defines permissible force using phrases like “reasonable” or “proportionate.”
In general, you can protect your house and belongings with more force. In some circumstances, fatal force is even permitted in some states. For example, when someone is trying to remove your personal property, you can protect it with non-lethal force. But you can’t break into your neighbor’s home or attack with a knife to get something back. Also, remember each case varies from the other depending on the situation. In some situations, a jury may judge your acts to be so careless that they grant the plaintiff punitive damages. They can also grant you punishment money, in exchange for your affirmative defenses.
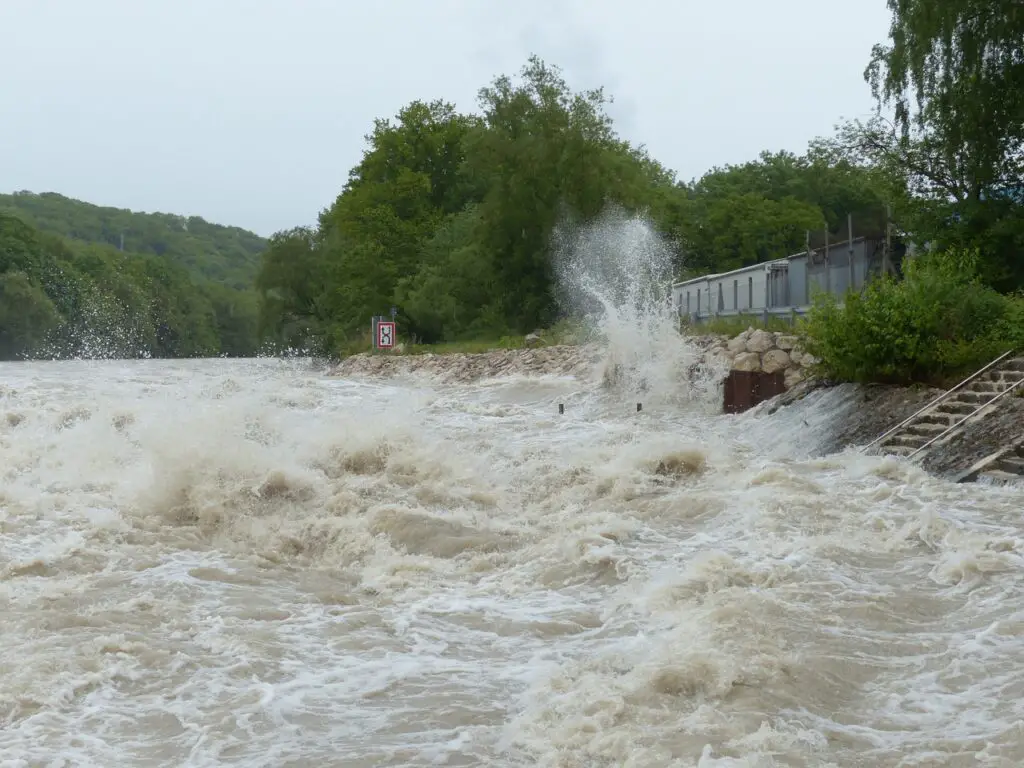
Analyzing the Case from the Lens of Law
In conclusion, this video highlights that what is seen through the eyes is not always a faithful representation of reality. If you closely examine the video, you will notice that the waves are actually in front of the camera. This indicates that the person filming the POV is moving behind something else and that something else is what is creating the waves. This shows that the reliability of the camera person in predicting or addressing the upcoming damages is now in question.

[…] offers insights on the vandalism consequences following a video of a lady causing a pole to tumble. The attorney’s perspective adds depth to understanding the legal ramifications. It sheds […]